Not all electric bikes are made equal. The type of motor an e-bike has plays a central role in how it feels to ride, its performance, and its cost.
Mid-drive motors are regarded as the premium choice for their superior ride feel and performance and thus are found on more expensive e-bikes. Conversely, hub motors are cheaper and easier to use but aren’t as smooth or high-performing.
Today, we are going to take a closer look at hub motors.
There are two categories of hub motors: direct-drive (gearless) and geared. The two designs have distinct strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different types of e-bikes.
However, geared hubs are considered superior in most cases and have largely replaced gearless motors across the industry.
This article will provide a detailed analysis of both hub motor designs to help you decide which suits your needs and preferences.
How Do E-Bike Hub Motors Work?
All e-bike hub motors consist of two sets of electromagnets. One set is fixed (the stator), and the other spins (the rotor). The stator’s magnets have coils attached; these are energized sequentially to create a magnetic field that spins the rotor, which connects to a shaft.
- Related guide: Hub Motor vs. Mid-Drive Motor Differences Explained
The torque generated by the spinning of the rotor drives the shaft. The shaft functions differently in each type of hub motor (gearless vs. geared). Firstly, let’s look closely at gearless hubs.
Direct Drive Motors (Gearless) Explained
In the gearless design, the motor’s shaft is also the wheel’s axle, so any generated torque directly drives the wheel. As a result, the shaft can only turn as fast as the wheel, limiting how much torque can be generated.
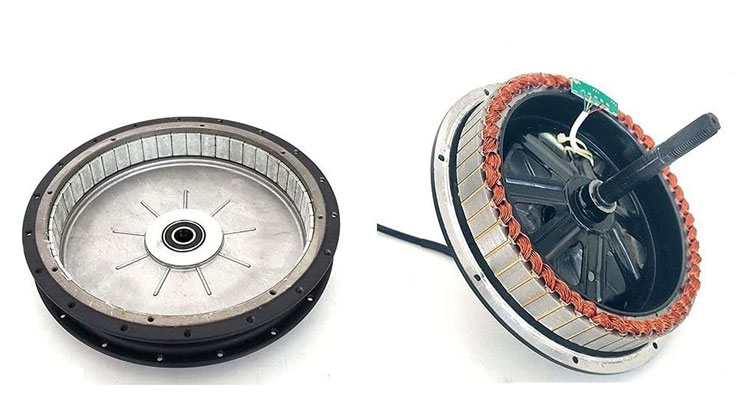
Direct-drive or gearless hub motors were the original widespread e-bike motor and are the simpler of the two. However, they are almost obsolete due to their limitations and narrow application.
Advantages of Direct Drive Motors:
The benefits of direct drives over geared hub motors are notable, given that they’ve mostly been phased out.
Most importantly, they are cheaper than geared hubs, and they can sustain higher max speeds with greater efficiency, so you’ll find them in low-cost e-bike conversion kits or on speed-optimized e-bikes.
These devices are also less mechanically complex, so they last longer and require less maintenance. This mechanical simplicity also means they run more quietly than geared hubs.
Finally, gearless hub motors are the only ones capable of regenerative braking.
Disadvantages of Direct Drive Motors:
Despite their advantages, the limitations of direct-drive motors have led to them falling out of favor.
Firstly, they are much heavier and bulkier than geared alternatives, which reduces the max range. Due to the limited torque output, these motors also have poor acceleration and hill-climbing capabilities. As a result, they’re not great for city riding.
In addition, because the motor’s shaft is the wheel axle, there is notable drag when pedaling without assistance.
Finally, the heavy motor in the wheel’s hub can negatively affect handling through uneven weight distribution.
Geared Hub Motors Explained
In contrast to direct drive motors, the shaft of a geared hub drives a set of fixed gears instead of driving the wheel axle directly. As a result of the reduction ratio, the shaft can turn much faster than the wheel (higher rpm), generating more torque.

Source: YouTube – Giesbert Nijhuis
This increased torque is beneficial for riding in urban environments as it is more efficient when the bike is moving at lower speeds and allows you to accelerate faster.
Advantages of Geared Rear Hub Motors:
As mentioned, geared hubs produce more torque, making them better for climbing hills and accelerating from a stopped position, which is ideal for best urban e-bikes and electric cargo bikes.
In addition, the lower weight and increased torque make geared hubs more efficient, getting more range from the battery.
Another significant advantage of these motors is that they are lighter and smaller, which reduces the bike’s total weight.
Finally, these motors also can freewheel without experiencing drag, which makes them better for riding without pedal assistance turned on.
Disadvantages of Geared Rear Hub Motors:
Geared hubs have a couple of noteworthy disadvantages compared to direct drives. Firstly, increased mechanical complexity means they require more maintenance and don’t last as long. They also tend to run louder.
The added efficiency at low speeds means they have lower max power outputs and are less efficient when riding at high speeds, draining the battery rapidly. Finally, the high torque in one wheel reduces traction control on loose or wet surfaces.
Performance Comparison of Direct Drive and Geared Hub Motors
Now that we’ve covered the pros and cons of both designs, let’s see how they compare head to head.
Power Output
Power is equal to torque multiplied by speed (rpm). Torque is the twisting force generated when the shaft inside the motor rotates.

Source: REI.com
Because the shaft in a geared hub motor can rotate very fast with the internal reduction gearing, it can generate more power at low speeds to move quickly from a stopped position or to overcome steep gradients. However, it must spin incredibly fast to maintain high power outputs, which is very energy-demanding.
In contrast, the shaft of a direct drive hub spins at the same speed as the wheel, so the wheel must turn at a high rpm for the power output to be high. However, once spinning quickly, the motor easily maintains and builds upon this higher power level, meaning that direct drives are more effective at high speeds.
Climbing Ability
High torque typically correlates to improved climbing ability, so geared hub motors perform better than direct drives when going uphill, as they can generate more torque at lower speeds.
Gearless hub motor e-bikes don’t climb well because the energy required to turn the wheel quickly and to overcome gravity and the extra weight of the motor and battery is incredibly high.
Efficiency
As mentioned, direct drive and geared hub motors have contrasting performance in terms of efficiency.
For example, geared hubs are more efficient than direct drives at low to moderate speeds (below 20mph). However, gearless motors are more efficient at higher speeds above 20mph, up to the Class 3 limit of 28mph.

For the above reasons, geared hub motors are said to be more efficient overall, as most riding on an e-bike is at or below 20mph.
In addition, riding at high speeds is extremely energy-demanding, regardless of how efficient the motor is at doing it. Therefore, direct drives typically have huge batteries to compensate for additional energy requirements.
Maintenance
E-bike motors don’t require much maintenance, but direct drive hubs are particularly low-maintenance as they are mechanically quite simple, meaning they should last a long time under normal usage conditions.
Adding an internal gearing system to geared hubs makes them more susceptible to issues over time. For example, the gears eventually wear down and need to be replaced.
Top Speed
The manufacturer limits the top speed of an e-bike based on local laws when they program the system. For example, in the US, e-bikes are restricted to 28mph (Class 3).

Again, in a gearless hub, the direct connection of the motor shaft to the wheel axle makes maintaining and building upon high speeds much more efficient. Conversely, a geared hub’s shaft must spin at a much higher rpm to generate the torque required to maintain high speeds, which uses energy more quickly.
The higher acceleration of geared hub motors allows them to reach their top speed faster.
Noise Level
Modern geared hub motors are not very noisy, especially the high-end systems such as Mahle’s Ebikemotion X35.
That said, they are louder than direct drives due to the internal movement and friction created by the gearing. Gearless hub motors are virtually silent.
Direct Drive vs. Geared Hub Motors: Which Should You Choose?
Direct drive and geared hub motors have distinct strengths and weaknesses, which helps when deciding which one suits your needs and preferences.
Budget
In general, direct-drive electric bikes are cheaper. Manufacturing the motors costs less because the technology is older and less complex. However, the almost ubiquitous use of geared hubs means they will likely be the cheaper option in the future.

Source: Vvolt.com
Very few manufacturers are still using direct-drive motors, with examples including Swiss brand Stromer, Cannondale, and other small-scale brands sold on Amazon.
Cannondale’s cheapest models use direct-drive hub motors, their more expensive hub-drive e-bikes have geared hubs, and their premium models have mid-drives. In contrast, Stromer’s bikes are all high-end with gearless hub motors.
Terrain and Riding Style
The type of terrain you tackle will help you determine which type of motor is best. For example, as described above, gearless hub motors have low torque levels, which means they aren’t as effective when riding uphill.
A geared hub motor is favorable if you like in a hilly area or undertake rides with lots of elevation gain. However, both work equally well if your rides are predominantly flat.
The type of riding you do and where you do it should also influence your decision. Geared hubs are better for commuting and city riding with lots of stopping and starting.
In contrast, if you do long-distance riding outside the city with fewer stops, the direct drive motor’s efficiency at high speeds may be favorable.
Desired Speed and Range
Geared hub motors are faster off the mark, thanks to their higher torque levels. In addition, they are more efficient at low to moderate speeds, so you’ll get more range, on average.

Direct-drive motors have greater top-end speed and efficiency at these speeds, so they are better suited for Class 3 ebikes (speed pedelecs). However, the batteries must be big to provide sufficient range for this type of riding. If not, the range will be low.
Weight of the Motor and Bike
Finally, because gearless hub motors are much heavier and require larger batteries, the bicycles are usually significantly heavier than geared hub e-bikes. Therefore, a lightweight geared hub is favorable if you want an e-bike that’s easy to carry.
Conclusion

In conclusion, the type of motor an ebike uses plays a crucial role in its performance, cost, and overall riding experience.
Although both direct-drive and gearless hub motors have their strengths and weaknesses, geared hubs are considered superior due to their increased torque, efficiency, and lighter weight.
Geared hubs are the preferred choice for urban e-bikes and electric cargo bikes as they provide more power at low speeds, making them better for climbing hills and accelerating from a stopped position.
Direct drives, on the other hand, are cheaper, simpler, and run more quietly but are more limited in their application due to their reduced torque output and added weight.
Ultimately, the choice of the motor comes down to personal preference and the intended use of the electric bike.
Read Next
E-Bike Modes Explained: Throttle vs. Pedal-Assist E-Bikes
E-Bike Classes Explained: What Do Class 1, 2 and 3 Mean?
Electric Bike Conversion Kits Guide

Your Feedback is Important!